For some time now, Facebook advertising has been recognized as a crucial strategy in the retail industry, enticing various types of retailers, including drop shippers, to invest in social media marketing, whether through omnichannel or multichannel approaches. With nearly 60 billion USD in advertising revenue generated in the US alone, it’s clear why this platform is a prime destination for advertisers.
To achieve favorable outcomes, Facebook advertising necessitates significant effort and diligence. Research and competitor analysis are also crucial, helping dropshippers create standout Facebook ads. Fortunately, Facebook’s Ads Manager provides essential support through an array of tools, including the invaluable Facebook ad metrics.
How Are Facebook Ads Measured?
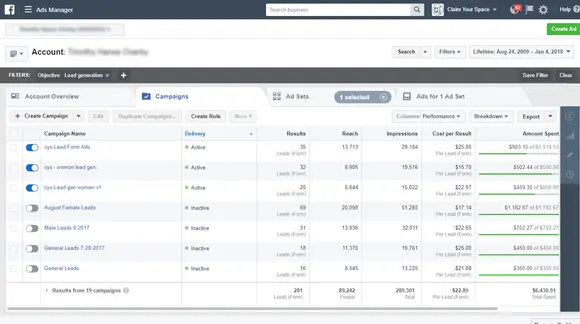
Facebook ads are evaluated using ad metrics, each employing different calculation methods based on what they measure (e.g., clicks, likes, views, budget). These metrics enable you to track your ads’ performance, analyze engagement, and calculate conversions.
What Key Metrics Should You Focus on for Facebook Ads?
With Ads Manager offering over a hundred ad metrics, selecting the most beneficial ones can be overwhelming. To simplify this, we’ve identified the essential Facebook ad metrics that will help you measure your ad campaigns success and create irresistible ads.
Detailed Explanation of Key Metrics
1. Amount Spent
This metric tracks the total amount of money you have spent on running your ad campaigns over a specific period. It provides insight into your financial commitment and helps in budgeting and financial planning.
Importance
- Budget Management: Knowing how much you've spent allows you to compare it against your budget, ensuring you don't overspend.
- Campaign Assessment: Helps in evaluating the return on investment (ROI) by comparing the amount spent to the revenue generated from the ads.
Use
- Control Costs: Regularly monitoring this metric helps you stay within your advertising budget and make necessary adjustments.
- Analyze Performance: By correlating spending with other performance metrics (like conversions or clicks), you can determine the cost-effectiveness of your campaigns.
2. Cost-Per-Click (CPC)
CPC measures the amount you pay each time someone clicks on your ad. It is calculated by dividing the total amount spent on the ad by the number of clicks received.
Importance
- ROI Measurement: A lower CPC means you are getting more clicks for less money, which generally indicates a higher ROI.
- Ad Efficiency: Helps assess the efficiency of your ad in generating interest and clicks.
Use
- Optimize Bidding Strategies: Adjust your bids to achieve a lower CPC while maintaining or improving ad performance.
- Improve Ad Content: A high CPC might indicate that your ad is not compelling enough, prompting you to refine your ad copy or visuals.
3. Cost-Per-Mile (CPM)
CPM, or Cost-Per-Thousand Impressions, measures the cost of 1,000 impressions (views) of your ad. It focuses on the visibility of your ad rather than direct interactions like clicks.
Importance
- Brand Awareness: Useful for campaigns aimed at increasing brand visibility and awareness.
- Cost Control: Helps you understand how much you are spending to get your ad seen by potential customers.
Use
- Targeting and Relevance: Ensure your ad is shown to the right audience to maintain low CPM.
- Creative Optimization: Optimize ad visuals and messaging to capture attention more effectively.
4. Cost-Per-Result (CPR)
CPR measures the cost of achieving a specific objective, such as a sale, sign-up, or any other predefined goal. It is the total amount spent divided by the number of times the objective was achieved.
Importance
- Objective Assessment: Directly ties ad spend to business goals, making it a key metric for performance evaluation.
- Budget Allocation: Helps in deciding where to allocate your budget for maximum impact.
Use
- Optimize Ad Strategies: Analyze which campaigns have the lowest CPR and refine strategies accordingly.
- Improve Targeting: Ensure your ads are reaching the right audience to achieve your objectives more cost-effectively.
5. Conversion Rate
Conversion rate is the percentage of users who completed a desired action (like making a purchase) after clicking on your ad. It is calculated by dividing the number of conversions by the total number of clicks.
Importance
- Performance Indicator: High conversion rates indicate effective ads and relevant audience targeting.
- ROI Calculation: Helps in calculating the overall ROI of your campaigns.
Use
- Landing Page Optimization: Ensure your landing pages are optimized for conversions.
- Refine Audience Targeting: Use data to target audiences that are more likely to convert.
6. Frequency
Frequency measures how often your ad is shown to the same user within a specific time period. It is calculated by dividing the total number of impressions by the number of unique users.
Importance
- Ad Recall: Higher frequency can improve brand recall and recognition.
- Ad Fatigue: Too high a frequency can lead to ad fatigue, where users start ignoring your ad.
Use
- Balance Exposure: Monitor frequency to ensure your ads are shown enough to be effective but not so much that they become annoying.
- Adjust Ad Rotation: Rotate ads or refresh creative content to maintain user interest.
7. Relevance
Relevance score measures how well your ad resonates with your target audience based on interactions and feedback (likes, shares, comments, and clicks). A higher relevance score generally means better ad performance.
Importance
- Cost Efficiency: Higher relevance often leads to lower costs and better placement in ad auctions.
- Audience Engagement: Indicates how engaging and useful your ad is to the audience.
Use
- Improve Targeting: Ensure your ads are relevant to the target audience by refining your targeting criteria.
- Optimize Content: Continuously improve your ad content based on feedback and performance.
8. Click-Through Rate (CTR)
CTR is the percentage of people who clicked on your ad after seeing it. It is calculated by dividing the number of clicks by the number of impressions.
Importance
- Engagement Metric: A higher CTR indicates that your ad is engaging and compelling enough to prompt clicks.
- Performance Indicator: Helps assess the effectiveness of your ad creative and messaging.
Use
- Ad Testing: A/B test different ad creatives and messages to find what generates the highest CTR.
- Refine Ad Content: Use insights from high-CTR ads to inform future ad designs and copy.
9. Link Clicks
Link clicks measure the number of clicks on links within your ad, directing users to various destinations like your website, landing page, or other external content.
Importance
- Traffic Measurement: Indicates how much traffic your ad is driving to your desired destinations.
- Ad Effectiveness: Helps evaluate the effectiveness of different ad elements (headline, image, call-to-action).
Use
- Optimize Call-to-Action: Ensure your call-to-action is clear and compelling.
- Improve Landing Pages: Make sure your landing pages are relevant to the ad content to maintain user interest.
10. Outbound Clicks
Outbound clicks count the number of clicks that take users to external sites from your ad.
Importance
- Traffic Generation: Measures the ability of your ads to drive external traffic.
- Performance Evaluation: Helps identify which ads and placements generate the most interest in external content.
Use
- Ad Placement Optimization: Focus on ad placements that generate higher outbound clicks.
- Content Relevance: Ensure the content on external sites aligns with user expectations set by the ad.
11. Post Engagement
Post engagement tracks all interactions with your ad, including clicks, comments, reactions, and shares.
Importance
- Engagement Indicator: High post engagement signifies that your ad is resonating well with the audience.
- Virality Potential: High engagement increases the likelihood of your ad being shared, thus reaching a wider audience organically.
Use
- Content Analysis: Use engagement metrics to understand what type of content resonates best with your audience.
- Enhance Interaction: Encourage interactions by asking questions or prompting discussions in your ad copy.
12. Return on Ad Spend (ROAS)
ROAS measures the revenue generated from your ad campaigns relative to the amount spent. It is calculated by dividing the revenue generated by the ad spend.
Importance
- Profitability Measurement: Directly indicates the profitability of your ad campaigns.
- Budget Justification: Helps justify ad spend by showing the financial return.
Use
- Campaign Optimization: Focus on campaigns with the highest ROAS and refine or discontinue underperforming ones.
- Budget Allocation: Allocate more budget to campaigns with higher ROAS for better overall returns.
Conclusion
Creating a successful ad campaign involves crafting visually appealing ads and utilizing Facebook ad metrics to evaluate performance. These metrics provide critical insights, enabling you to optimize your ads and achieve your marketing goals effectively.
What to read next

